Unreal Engine Plugin Overview
DataTables work — until they don’t.
A flat CSV-backed table handles a list of weapons just fine. But the moment a Quest needs to reference
three Items, each with variant stats that inherit from a base type, with display text in four languages —
DataTables hit a wall. You end up with parallel tables held together by string row names, a Blueprint
full of GetDataTableRow nodes, and struct definitions that go stale the moment a designer adds a field.
Unreal’s data tools were built for simplicity, not for scale. The Charon Unreal Plugin is built for exactly the kind of complex, relational, multi-language game data that real productions demand — with native C++ and Blueprint access and zero boilerplate.
What is it?
The Charon Unreal Plugin is a relational game database embedded in the Unreal Editor. It gives you:
A schema-driven data model — define your
Hero,Item,Questtypes once, with typed fields, inheritance, and cross-references between themA visual editor that opens directly from the Content Drawer — same workflow designers already know, no new tools to learn
Automatic C++ and Blueprint generation — every time your schema changes, your struct definitions and access code update themselves
It is the data layer your game needs without the infrastructure you’d have to build to get there.
Which problem does it solve?
Pain Point |
How Charon Fixes It |
|---|---|
DataTable limitations |
Full relational model: nesting, inheritance, and cross-table references without string row-name fragility. |
Struct boilerplate |
C++ structs and Blueprint nodes are generated automatically — change a field in the editor, not in code. |
Broken cross-references |
Referencing a deleted row is a validation error, caught before the build, not at runtime. |
Designer bottleneck |
A purpose-built UI lets designers tune values and write content without touching C++ or Blueprints. |
Localization complexity |
|
Live-ops friction |
Dynamic data loading via |
Who is it for?
- Technical Directors & Programmers
Generated C++ structs give you type-safe data access with full IDE support and no parsing logic. The CLI and REST API plug directly into your CI/CD pipeline — validate data on every commit, diff between versions, automate patch builds.
- Game & Narrative Designers
Build complex item economies, branching quest trees, and character progressions in a structured editor — without writing a line of C++ or creating Blueprint spaghetti. Validation catches broken references before they reach a programmer.
- Live-Ops Teams
Load updated game data at runtime without a store submission. Roll back a bad balance change in minutes. Ship localization updates as data patches, not engine builds.
Key Features
Feature |
Benefit to Your Workflow |
|---|---|
C++/Blueprint Generation |
Access your data instantly with full IDE auto-complete and Blueprint nodes. |
Relational Modeling |
Interconnect tables (Items, Quests, NPCs) with ease within a single UI. |
Hot Updates |
Support for dynamic loading of game data for live-tuning and hotfixes. |
Modding Support |
Give your community the same professional tools to create game mods. |
Localization |
Seamlessly export and import translation keys for global releases. |
Getting Started
To begin using this plugin, the initial step involves installing the plugin from the Unreal Engine Marketplace. Once installed, you’ll need to enable the plugin for your project through the project settings. Following this, a rebuild of your project’s C++ code is necessary. The final step in the setup process is the creation of your first game data file.
Prerequisites
The Unreal Engine plugin is written in C++ but relies on dotnet charon, a .NET Core application which runs on .NET 8.
Download and install SDK NET 8+.
Make sure you have write access to
%PROGRAMDATA%/Charon.
Download and install SDK NET 8+.
Make sure you have write access to
/Users/<username>/.config/Charon.Make sure
dotnetis available from$PATH.
Linux
Download and install NET SDK 8+.
Make sure you have write access to
/home/<username>/.config/Charon.Make sure
dotnetis available from$PATH.
Checking Available .NET SDK Versions
# check for dotnet already installed
dotnet --list-sdks
# output for dotnet --list-sdks
7.0.120 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\sdk]
8.0.206 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\sdk]
8.0.414 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\sdk] # <- this one is fine
9.0.300 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\sdk] # <- this one too
Installation from Marketplace
Add to cart Charon plugin [Epic Launcher] / [Fab.com Asset Page] in the Unreal Engine Marketplace.
Follow the instruction on installing plugin into your project:
Click Install to Engine and select the engine version.
Open your project and go to Edit → Plugins… window.
Type Charon in the Search bar.
Check the checkbox near the plugin’s name to enable it.
Rebuild project C++ code.
Building from Source Code
Clone or download the plugin source code from the GitHub repository.
Create a
<project-dir>/Plugins/Charondirectory.Copy the plugin files into this directory. Ensure Charon.uplugin is located at the path
<project-dir>/Plugins/Charon/Charon.upluginafter copying.Remove the
"EngineVersion"attribute if your engine doesn’t match the plugin’s engine version.Rebuild the project’s C++ code.
Enable the plugin in Edit → Plugins… if needed.
Core Concepts
Data-Driven Design Principles
The rule is straightforward: if a designer might want to change it, it belongs in data — not in C++ and not in a Blueprint.
Damage formulas, AI behavior thresholds, loot table weights, narrative branch conditions — when these live in code, every balance pass requires an engineer. When they live in structured data, a designer can iterate in an afternoon without touching the build.
Unreal Engine has always encouraged this approach. DataTables, UDeveloperSettings, and config files are all steps in that
direction. Charon takes it further: a full relational model with validation, generated access code, and a UI that non-technical
team members can use confidently.
The payoff compounds over time:
During production: balance changes and content additions don’t block engineering
At ship: every game value is version-controlled, auditable, and rollback-able
Post-launch: mods, live patches, and A/B tests are data operations, not code releases
Further reading:
Understanding the Plugin’s Architecture
Plugin Assets
Working with data in this plugin is akin to how the built-in DataTable functions. There is a data source file, a module containing the code required to load the data, and an asset that will be utilized in the game. Whenever you edit a data source file, you need to re-import this data into the asset. Should the data structure in the source file change, then the C++ code must be regenerated.
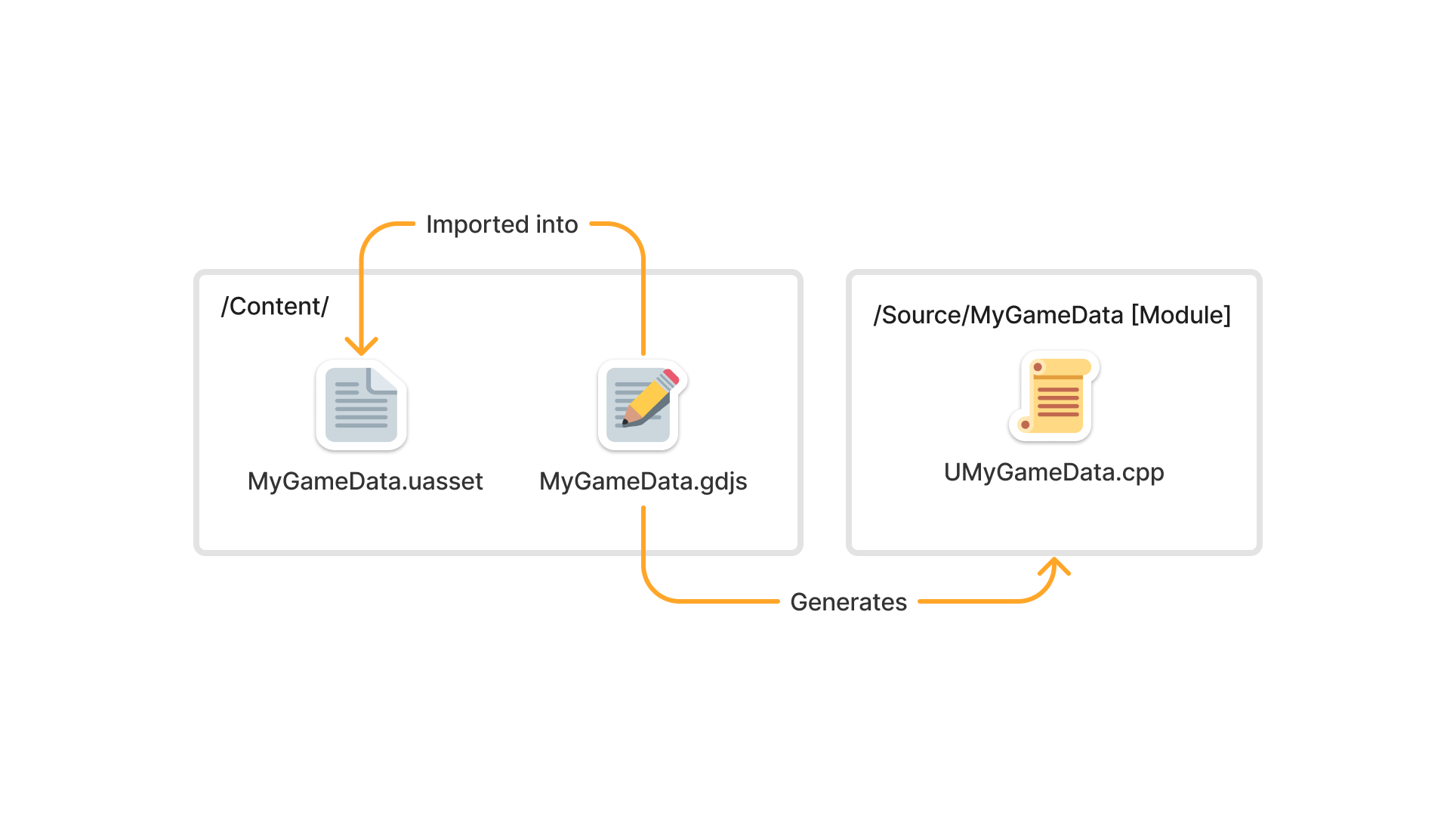
For scenarios requiring dynamic loading of game data, this can be accomplished through the TryLoad method on the game data class, which accepts the source JSON file.
Plugin Modules
- The Charon plugin is structured into two modules:
CharonEditormodule acts as an Unreal Engine Editor extension. Extension points for the module are declared in theICharonEditorModuleclass, and automation of game data processing is facilitated through theFCharonCliclass.Charonmodule, houses the core logic and shared code crucial for handling game data files.
Working with the Plugin
Creating Game Data
To create a new game data file within the Unreal Engine Editor, open the Content Drawer, right-click in the desired folder, and select in the Create Advanced Assets section Miscellaneous → Game Data menu option. Name your game data file and proceed according to the instructions in the dialog window that appears.
Editing Game Data
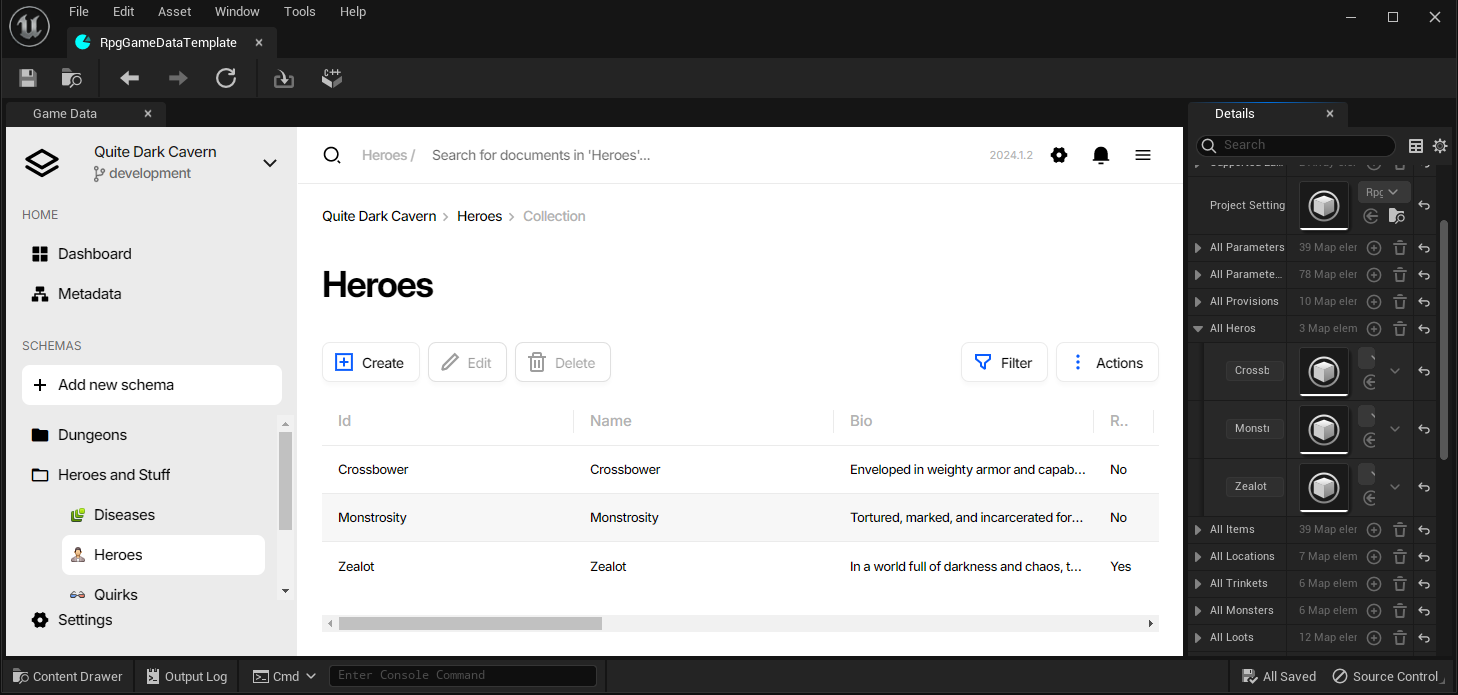
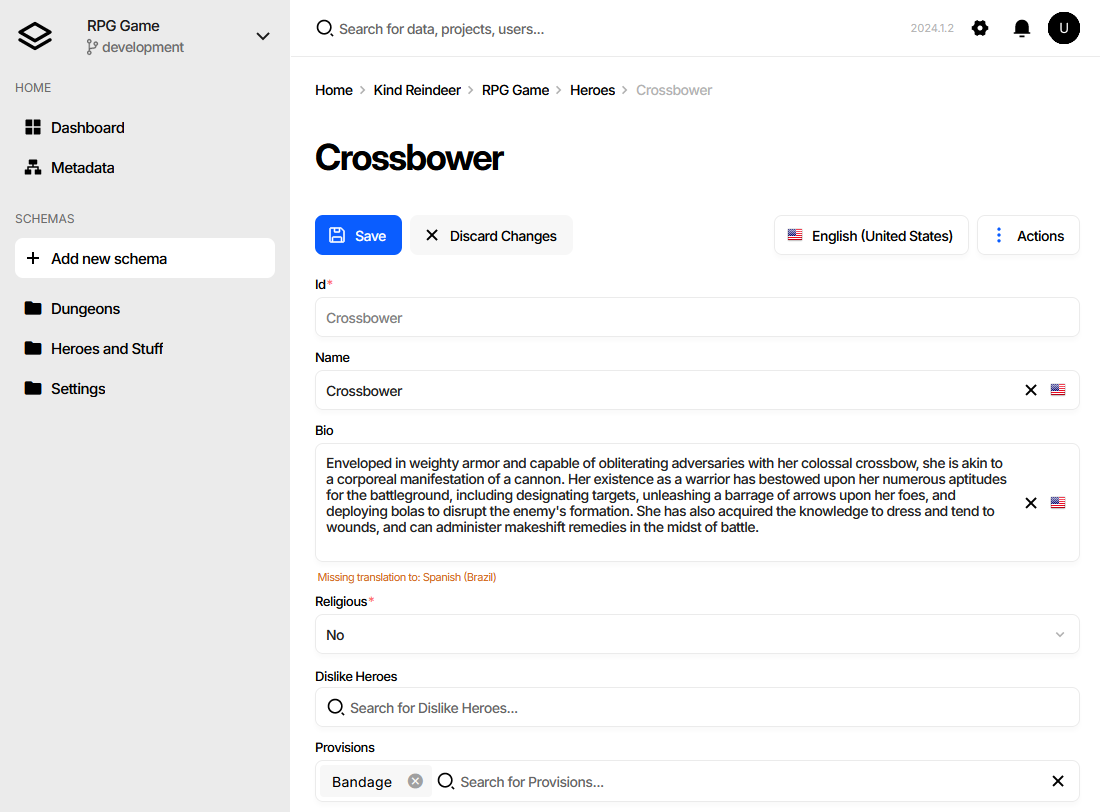
To edit a game data file in the Unreal Engine Editor, navigate to the Content Drawer, find the corresponding .uasset file, and double-click it. This action opens a new window featuring a user interface for editing the game data. Remember to reimport and, if necessary, regenerate the source code after completing your edits.
Referencing Game Data in Blueprints
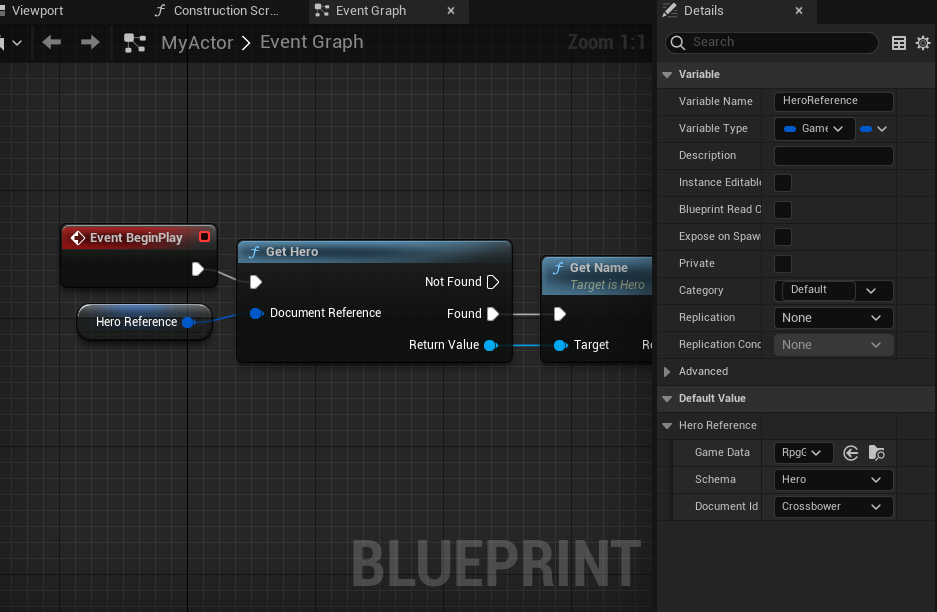
Similar to the DataTable’s FDataTableRowHandle, the Charon plugin introduces a specific type for referencing documents within Blueprints,
named FGameDataDocumentReference. This type is housed within the Charon module. Here is example of Game Data Document Reference used to resolve Hero document:
Advanced Features
Localization and Multi-Language Support
Charon facilitates multi-language text support through the Localizable Text data type. When creating a Schema, properties can be defined with various data types, including Localizable Text.
Initially, all localizable text defaults to EN-us (US English). Additional languages can be added via Project Settings → Internationalization → Translation Languages in the Charon UI.
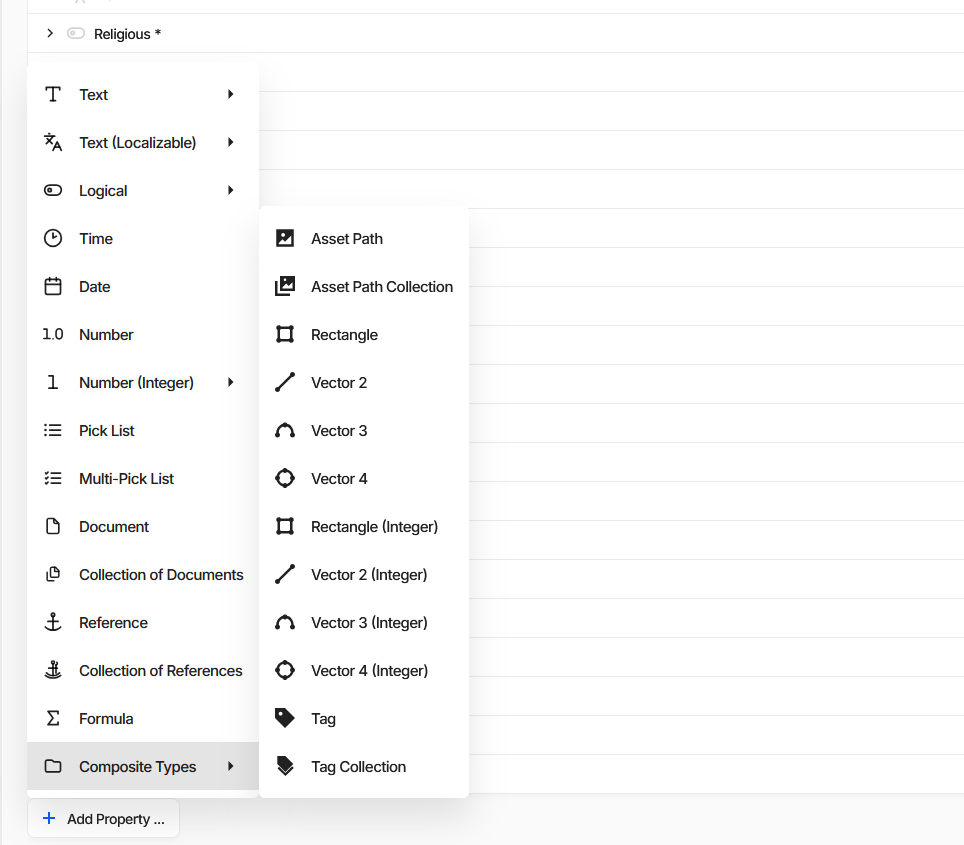
Referencing Unreal Engine Assets
To reference assets within the game, you can use a special Asset composite type. Create a property via Composite Types -> Asset Path menu options.
Feedback
We welcome and encourage feedback, particularly bug reports and suggestions, to help improve our tool. If you have any questions or would like to share your thoughts, please join our Discord community or reach out to us via email at support@gamedevware.com.